Joint Crediting Mechanism
Joint Crediting Mechanism
About JCM
Basic Concept of the Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM)
- Facilitating diffusion of leading decarbonization technologies, products, systems, services, and infrastructure as well as implementation of mitigation actions, and contributing to sustainable development of developing countries.
- Appropriately evaluating contributions from Japan to GHG emission reductions or removals in a quantitative manner and use them to achieve Japan's emission reduction target.
- Contributing to the ultimate objective of the UNFCCC by facilitating global actions for GHG emission reductions or removals.
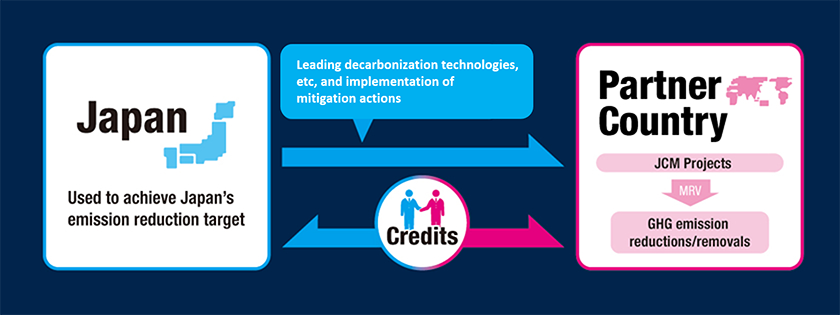
Japan establishes and implements the JCM in order to quantitatively evaluate contributions of Japan to greenhouse gas emission reductions and removals which are achieved through the diffusion of, among others, leading decarbonizing technologies, products, systems, services, and infrastructures as well as through the implementation of measures in developing countries and others, and in order to use such contributions to achieve Japan’s NDC. By doing so, through public-private collaborations, Japan aims to secure accumulated emission reductions and removals at the level of approximately 100 million t-CO2 by fiscal year 2030. Japan will appropriately count the acquired credits to achieve its NDC. As of February 2024, Japan has established the JCM with 29 partner countries (Mongolia, Bangladesh, Ethiopia, Kenya, Maldives, Viet Nam, Lao PDR, Indonesia, Costa Rica, Palau, Cambodia, Mexico, Saudi Arabia, Chile, Myanmar, Thailand, Philippines, Senegal, Tunisia, Azerbaijan, Moldova, Georgia, Sri Lanka, Uzbekistan, Papua New Guinea, United Arab Emirates, Kyrgyz, Kazakhstan and Ukraine).
The rules and guidelines adopted under the Joint Committee established by Japan and each partner country as well as up-to-date information on methodologies and projects are uploaded on the JCM website.
Relevant documents of the JCM
| Date | Title |
|---|---|
| May, 2024 | Recent Development of the Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM) |
| October, 2022 |
Japan's Submission Article 6 of the Paris Agreement |
| October, 2021 | Japan’s Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) |